(IoT) Internet of Things

Many of today’s infrastructure was designed and built in an analog era and built before it was possible to integrate sensors or to build better, more cost-effective energy, water, logistics or transport infrastructure and much before cars might talk to the road, or drive on their own Today everything that can be connected will be connected, as an ‘Internet of Things’ (IoT).
The key is the interconnection via the Internet of computing devices embedded in everyday objects, enabling them to send and receive data... "if one thing can prevent the Internet of things from transforming the way we live and work, it will be a breakdown in security"
Cloud Computing PARADIGM has emerged disrupting traditional “Value Chains”, allowing unprecedents “economies of scale” and consolidating the ”techological democracy” concept to result of the eroding of “entry barriers” to ”state of the art” technology infrastructure.
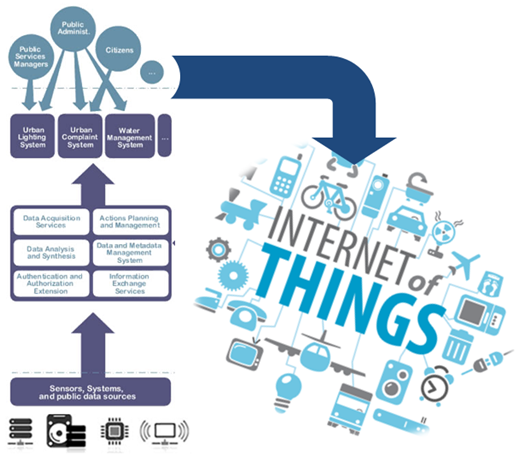
Cloud Technology has enabled the advent of the "Internet of Things", having understood that things themselves produce information, whose obtaining -by means of sensors, devices, etc.- and subsequent use produce results of maximum richness and direct impact on the processes optimization.
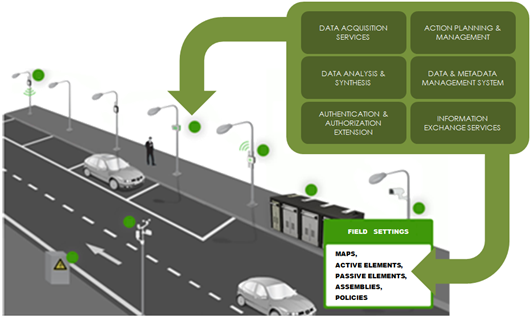
The ability to connect devices and interpret them means that IoT can have unlimited applications, can act in almost any area and be responsible for collecting information in multiple environments: from living beings and natural ecosystems to buildings and vehicles, so they could be used for any type of behavior monitoring, both environmental and urbanistic